Audio Files
Just like when using Meshes or Textures, the workflow for Audio File assets is designed to make things work for you quickly and easily. You can make your Audio Files with any format you like, and Unity can import them and play them back, but there's some specific information you should know for working with Audio Files.
Audio in Unity is either Native or Compressed. Unity support the most common formats (see list after this). Just drag the file into the Editor to import the file. The default mode is Native and Unity just uses the original file. Unity can also compress the supplied file. Choose the Compressed option in the importer. (Unity IPhone can make use of the hardware decoder. See IPhone specific documentation for this). The difference between Native and Compressed is outlined here:
- Compressed: Compress sounds by choosing the compressed option from inside the Editor. The audio data will be small, but will cost CPU cycles to decode at play time. Depending on the target, Unity will encode the audio to either Ogg Vorbis(Mac/PC/Consoles) or MP3 (Mobile platforms). For the best sound quality supply the audio in an uncompressed format such as WAV or AIFF (containing PCM data) and let Unity do the encoding. If only targeting Mac/PC (standalones, webplayers) importing an Ogg Vorbis file will not degrade the quality. But converting to mobile platforms will force a re-encode to MP3 and cause a slight quality degradation. Same goes for importing MP3, when only targeting mobile platforms.
- Native: Use Native (WAV, AIFF) audio for short sound effects. The audio data will be larger, but sounds won't need to be decoded at play time.
Any Audio File imported into Unity is an Audio Clip. Audio Clips work in conjunction with Audio Sources and an Audio Listener. Think of Clips as audio data only. When you attach your Clip to an object in the game, it becomes an Audio Source and it now has Volume, Pitch, and a wealth of other properties. While a Source is playing, an Audio Listener can "hear" all Sources that are close enough, and those are the sounds you will hear through your speakers. There can be only one Audio Listener in your scene, and this is usually attached to the Main Camera. In most cases you will work with Audio Sources more than Clips or Listeners.
Supported Formats
| Format | Compressed as (Mac/PC) | Compressed as (Mobile) |
|---|---|---|
| MPEG(1/2/3) | Ogg Vorbis | MP3 |
| Ogg Vorbis | Ogg Vorbis | MP3 |
| WAV | Ogg Vorbis | MP3 |
| AIFF | Ogg Vorbis | MP3 |
| MOD | - | - |
| IT | - | - |
| S3M | - | - |
| XM | - | - |
See the Sound chapter in the Creating Gameplay section of this manual for more information on using sound in Unity.
Audio Clip
Audio Clips are audio data used by Audio Sources. Unity supports mono, stereo and multi (up to 8) channels audio assets. Unity supports importing the following audio file formats: .aif, .wav, .mp3, and .ogg, and the following tracker module file formats: .xm, .mod, .it, and .s3m. The tracker module assets works the same way as any other audio assets in Unity except waveform preview can be rendered to the asset import inspector.
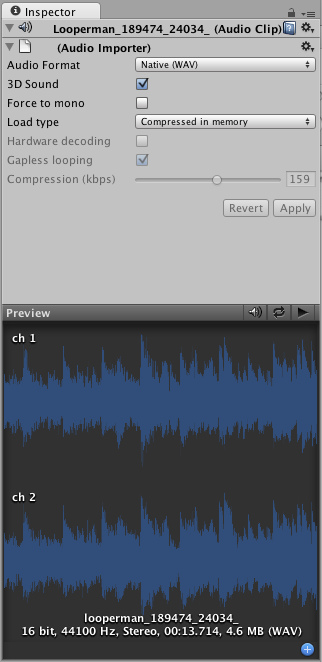
The Audio Clip Inspector
Properties
| Audio Format | The specific format that will be used for the sound at runtime. |
| Native | Larger file size, higher quality. Best for very short sound effects. |
| Compressed | Smaller file size, lower/variable quality. Best for medium length sound effects and music. |
| 3D Sound | If enabled, the sound will play back in 3D space. Both Mono and Stereo sounds can be played in 3D. |
| Force to mono | If enabled, the audio clip will be down-mixed to a single channel sound. |
| Load Type | The way Unity load audio assets runtime. |
| Decompress on load | Decompress sounds upon load. Use this for smaller compressed sounds to avoid the performance overhead of decompressing on the fly. Beware that a compressed sound will use ~10x more memory that when decompressed, so don't use this for large files. |
| Compressed in memory | Keep sounds compressed in memory and decompress while playing. This have a slight performance overhead (esp. for Ogg/Vorbis compressed files) so only use this for bigger files. |
| Stream from disc | Stream audio data directly from disc. This uses a fraction of the original sounds size of memory. Use this for your music or very long tracks. Depending on the hardware, a general advice is to keep this down to 1-2 simultaneously streams. |
| Compression | Amount of Compression to be applied to a Compressed clip. Statistics about file size can be seen beneath the slider. It is suggested to drag the slider to a place that leaves the playback "good enough" but still at a small enough size to meet your file size/distribution needs. |
| Gapless looping | (Android/iOS ONLY) Use this when compressing a perfect looping audio source file (in a non-compressed PCM format) to preserve the loop. Standard MPEG encoders introduce silence around the loop point, which will play as little "click" or "pop". Unity handles this smoothly for you. |
Importing Audio Assets
Unity supports both Compressed and Native Audio. Any type of file (except MP3/Ogg Vorbis) will be initially imported as Native. Compressed audio files must be decompressed by the CPU while the game is running, but are smaller in file size. If Stream is checked the audio is decompressed on the fly, or else the audio is decompressed entirely upon load. Native PCM formats (WAV, AIFF) have the benefit of being higher fidelity without increasing CPU taxation, but create much larger files. Module files (.mod,.it,.s3m..xm) can deliver very high quality with an extremely low footprint.
As a general rule of thumb, Compressed audio(or modules) are best for long files like background music or dialog, and uncompressed is better for short sound effects. Tweak the amount of Compression with the compression slider to just before the difference in sound quality is noticeable.
Using 3D Audio
If an audio clip is marked as a 3D Sound then it will be played back to simulate its position in the game world's 3D space. 3D sounds emulate distance and location of sounds by attenuating volume and panning across speakers. Both mono and multiple channel sounds can be positioned in 3D. For multiple channel audio, use the spread option on the Audio Source to spread and split out the discrete channels in speaker space. Unity offers a variety of options to control and fine-tune the audio behavior in 3D space. Take a look at Audio Source.
Platform specific details
 Android
Android
On mobile platforms compressed audio is encoded as MP3 for less CPU intensive decompression.